Kymera’s pipeline is focused on addressing disease targets where there is significant patient need and where we believe protein degradation is the only or best way to improve the standard of care.
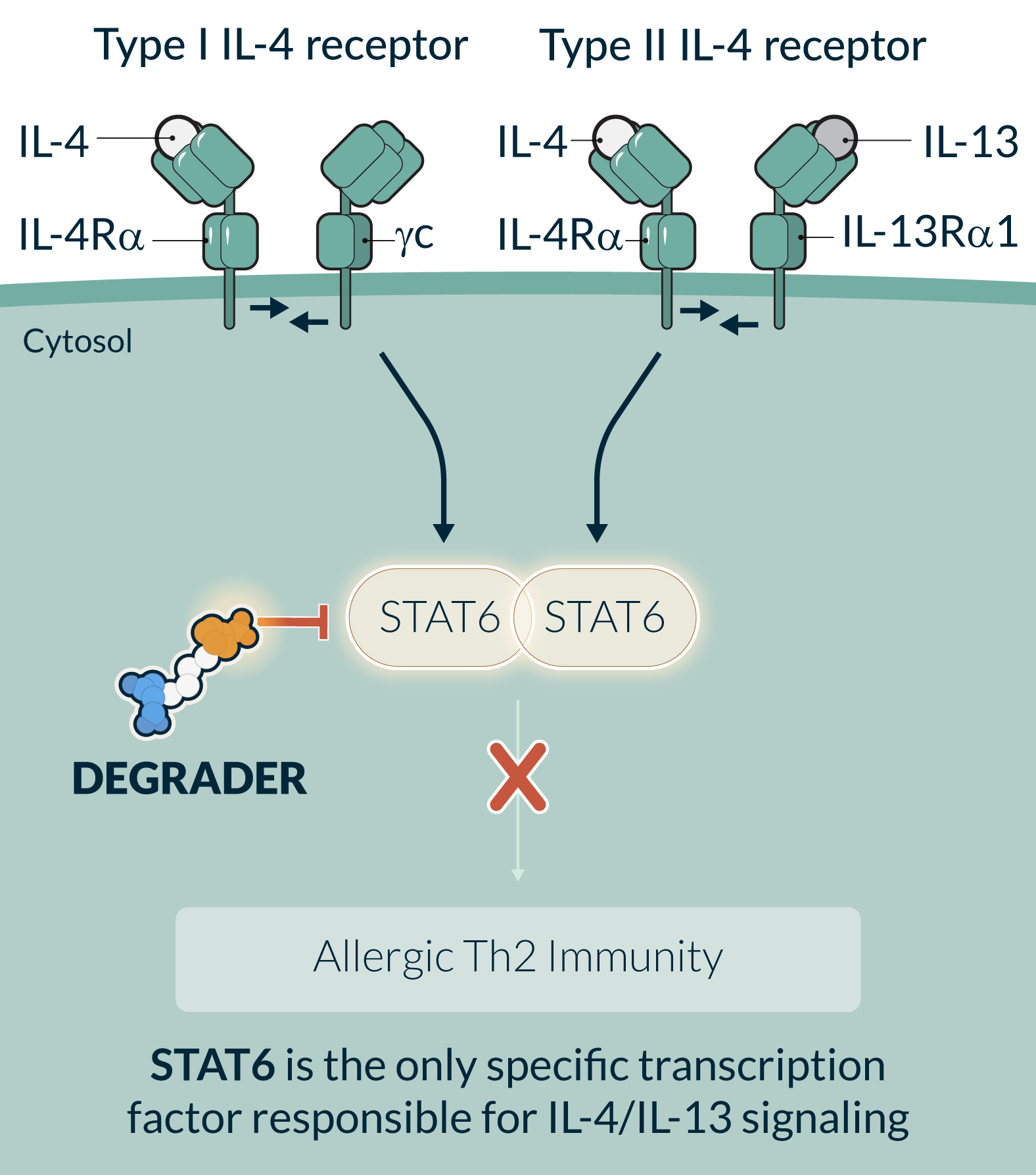
STAT6 is an essential transcription factor in the IL-4/IL-13 signaling pathways and the central driver of Type 2 inflammation in allergic diseases. Multiple gain of function mutations of STAT6 were identified to cause severe allergic diseases in humans. Dupilumab, an injectable monoclonal antibody that blocks IL-4/IL-13 signaling, is an approved therapy for multiple diseases. STAT6 targeting is therefore supported by both human genetics and clinical pathway validation. STAT6 functions through protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions and it has been challenging to selectively and potently inhibit STAT6 with small molecule inhibitors. However, it is well suited for a targeted protein degradation approach, where a binding event is sufficient to drive degradation. STAT6 degradation has the potential to provide the convenience of an oral medicine with the potential for biologics-like activity and in doing so reach broader patient populations compared to injectable biologics or other standards of care.
KT-621 is an investigational, first-in-class, once daily, oral degrader of STAT6. In preclinical studies, KT-621 demonstrated full inhibition of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway in all relevant human cell contexts with picomolar potency that was superior to dupilumab, and equivalent or superior efficacy to dupilumab in multiple preclinical efficacy studies. In the Phase 1b clinical study in atopic dermatitis patients, KT-621 demonstrated deep STAT6 degradation in blood and skin, robust reductions in disease-relevant Type 2 inflammatory biomarkers, meaningful improvements on clinical endpoints and patient-reported outcomes in AD and comorbid asthma and allergic rhinitis, and was well tolerated with a favorable safety profile.
KT-621, the first STAT6-targeted medicine to enter clinical evaluation, has the opportunity to transform treatment paradigms for more than 140 million patients around the world suffering from Type 2 diseases.
Atopic Dermatitis
Asthma
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Eosinophilic Esophagitis
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps
Chronic Spontaneous Urticaria
Prurigo Nodularis
Bullous Pemphigoid
Others
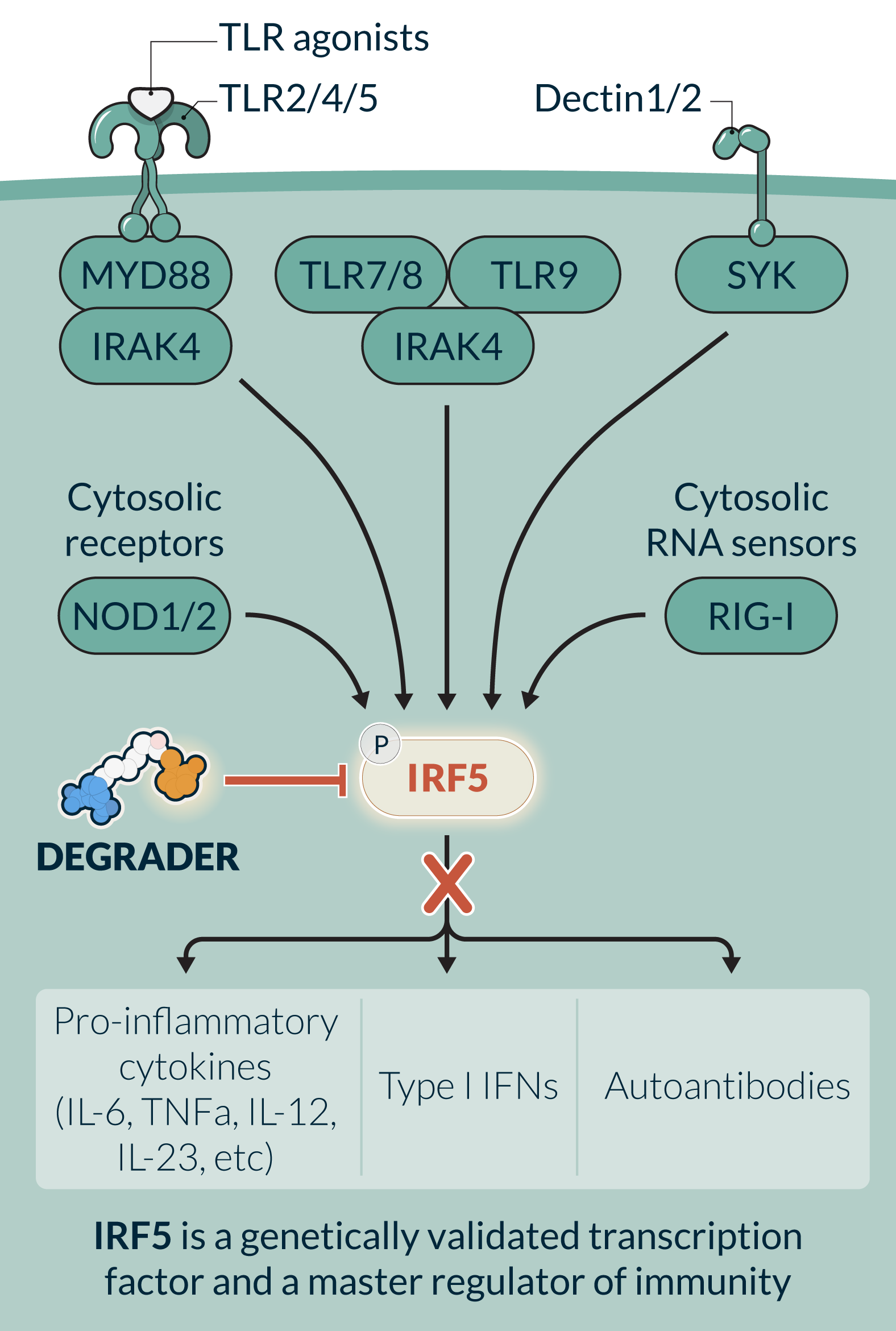
IRF5, a historically undrugged transcription factor, is a master regulator of innate and adaptive immune response pathways involving pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNFα, IL-6, IL-12, IL-23), B cell activation (autoantibody production), and Type I Interferon (IFN). IRF5 is selectively expressed and activated in specific cell types such as dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages, and B cells. Its cell- and disease activation-specific profile has the potential to block cell-specific immune dysregulation while sparing normal cell function. IRF5 has been challenging to drug using traditional small molecule inhibitors due to multiple complex activation steps and the high degree of IRF family member homology. KT-579, a potent, selective oral degrader, has the potential to be the first IRF5-targeted therapy. In preclinical studies KT-579, degraded IRF5 across multiple preclinical species and in all disease-relevant tissues. In preclinical models of lupus and RA, KT-579 was equal or more efficacious than clinically active or marketed small molecule inhibitors and biologics. In preclinical safety studies, KT-579 did not show any adverse effects at concentrations up to 200-fold of the projected human efficacious levels. KT-579 has the potential for broad utility in diseases where effective and well tolerated oral therapies are needed.
Lupus
Sjögren’s Syndrome
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Systemic Sclerosis
Dermatomyositis
Others
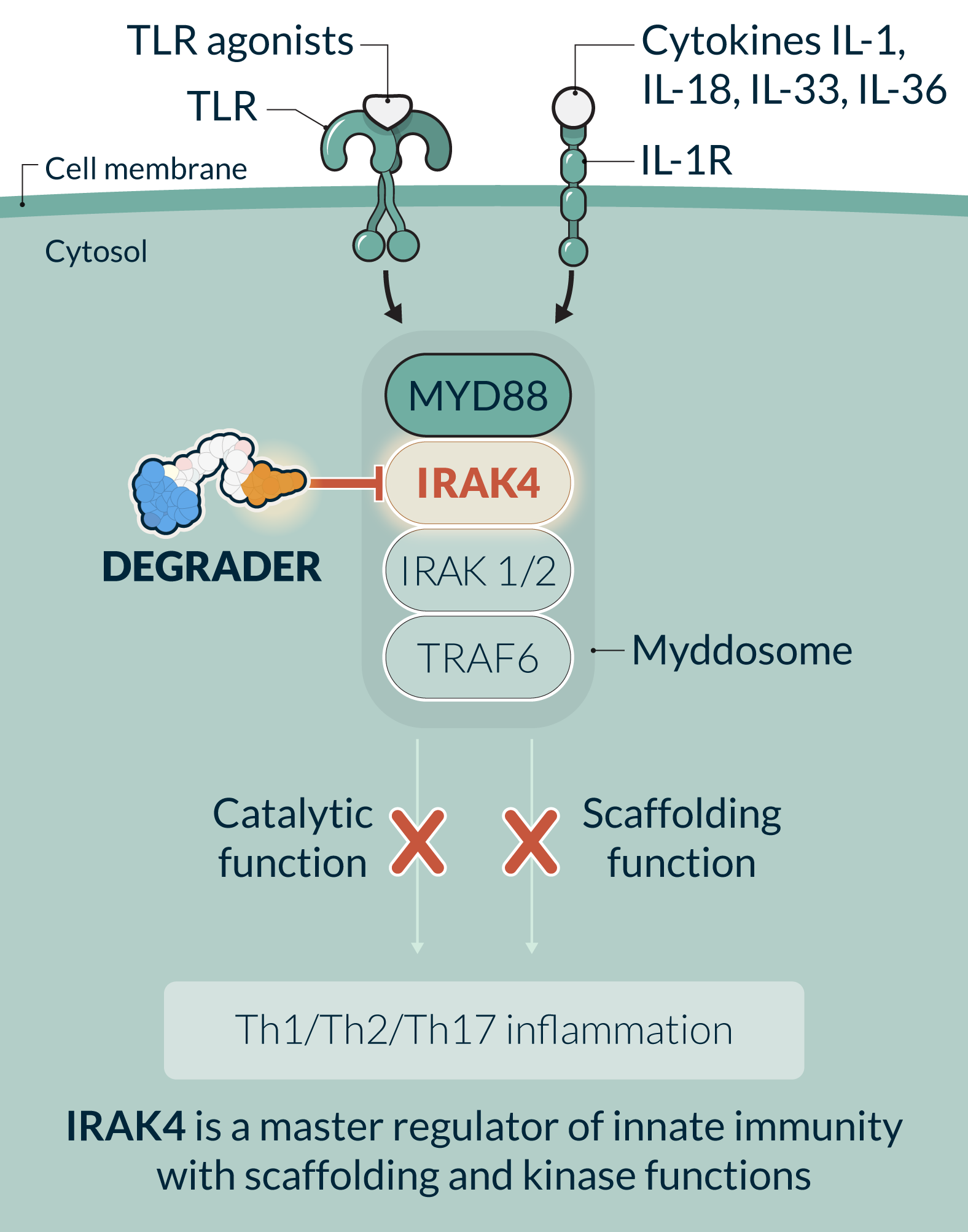
KT-485 (SAR447971) is a first-in-class, selective, potent, oral IRAK4 degrader in development for the treatment of immuno-inflammatory diseases with significant patient need. KT-485, a second-generation IRAK4 degrader developed by Kymera, has increased potency and specificity over the first-generation IRAK4 degrader, KT-474, and has been prioritized by Sanofi for further clinical development. Before this prioritization decision, KT-474 had completed Phase 1 studies in healthy volunteers and HS and AD patients. IRAK4 is a master regulator of innate immunity and key protein of the myddosome complex that mediates signaling through IL-1 and toll-like receptors. IRAK4 is a scaffolding kinase that acts at the interface of the innate and adaptive immune responses with a variety of functions depending on its kinase activity and scaffolding function. Eliminating IRAK4 completely through degradation impacts both the kinase and scaffolding functions, therefore having the potential to achieve a broad, well-tolerated, anti-inflammatory effect providing a novel therapeutic approach for a variety of immune-inflammatory diseases. Clinical data generated to date demonstrates the potential of IRAK4 degradation to deliver the combined activity of upstream biologics in an oral drug for multiple diseases.
Sanofi, which is collaborating with Kymera on the development of IRAK4 degraders outside of the oncology and immuno-oncology fields, is progressing the IRAK4 program through clinical development. Kymera has the option to participate in future development and commercialization, and 50/50 profit split, in the United States. Double digit tiered royalties in ROW.
Diseases where the TLR/IL-1 pathway has been implicated in pathogenesis and are potential opportunities: HS, AD, Psoriasis, Generalized Pustular Psoriasis, IBD, Asthma, COPD, SSc ILD, RA, PSA, SLE, OA, PSS, MS, AMD.
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2) is a master regulator of the cell cycle with strong genetic and clinical validation. Gene amplification and over-expression of CCNE1, which encodes cyclin E1, drives aberrant CDK2 activity in cancer and promotes tumor growth. CCNE1 amplification and over expression is associated with resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors in breast cancer and other solid tumors. CDK2 active-site inhibitors have proven activity in CCNE1-amplified tumors, but frequently suffer from poor CDK selectivity, particularly against CDK1, contributing to narrow therapeutic margins. Unlike inhibitors, CDK2 molecular glue degraders selectively degrade CDK2 while sparing closely related kinases like CDK1, offering a potentially broader therapeutic index
Kymera and Gilead Sciences have an exclusive option and license agreement to accelerate the development and commercialization of a novel molecular glue degrader program targeting CDK2 with broad oncology treatment potential including in breast cancer and other solid tumors. Kymera will lead all research activities for the CDK2 program. If Gilead exercises its option to exclusively license the program, Gilead will have global rights to develop, manufacture and commercialize all products resulting from the collaboration.
When appropriate, we partner with leading global pharmaceutical companies to maximize the reach of our degrader programs and develop transformative therapies for the broadest possible patient populations.
Our partnership with Sanofi is designed to accelerate the path to broader clinical development and commercialization of our oral, first-in-class protein degrader therapies targeting IRAK4 in patients with immune-inflammatory diseases.
Our partnership with Gilead is designed to accelerate the path to clinical development and commercialization of oral molecular glue degrader therapies targeting CDK2 for broad oncology treatment potential including in breast cancer and other solid tumors.

